Learn More about Phytonutrients
Phytonutrients are compounds found in plants. “Phyto” refers to the Greek word for plant.
These amazing compounds serve many important functions in plants, helping to protect the plant’s ability to exist. Some phytonutrients protect the plant from UV radiation while others can protect it from insect attack. Phytonutrients award benefit to the plants but where they really rock is for those who enjoy eating the whole food nutrition of plant food. That’s because they have properties that boost and promote health-promoting activities and they have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits as well.
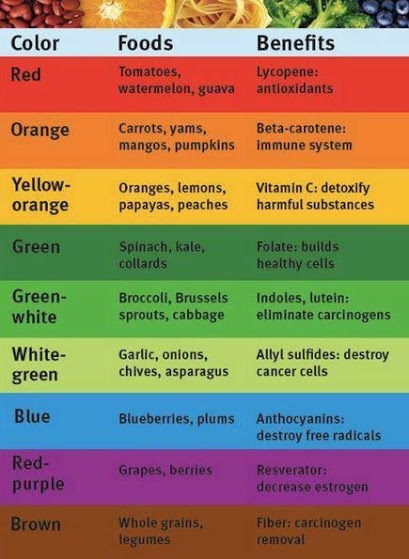
Blueberries, blackberries and red cabbage (rich in flavonoids); yellow-orange sustenances like carrots, winter squash, papaya, and melon (rich in beta-carotene); red or pink nourishments like tomatoes, guava, and watermelon (rich in lycopene); and green nourishments like kale, spinach, and collard greens (rich in chlorophyll). Yet, since not all phytonutrients give color, its essential to not neglect some off-white nourishment too for instance, garlic, onions, and leeks are rich in compelling sulfur-holding phytonutrients. Phytonutrients aren’t essential for keeping you alive, unlike the vitamins and minerals that plant foods contain. But when you eat or drink phytonutrients, they may help prevent disease and keep your body working properly.


However, in the process of being broken down, these phyto-nutrients send a signal to our DNA to produce specific proteins, called “enzymes,” that can break down both these phytonutrients and some Phytochemicals Block the Cancer Process toxins produced in our cells or taken in from our diet. As you can imagine, only those toxins that have chemical structures in common with the phytonutrient in a particular fruit or vegetable are detoxified. So it makes sense to take in as diverse a group of plant foods as possible.
David Heber, M.D., Ph.D.
More than 20,000 phytonutrients are found in plant foods. There are six important phytonutrients they are: Carotenoids, Ellagic acid, Flavonoids, Resveratrol, Glucosinolates and Phytoestrogens.
More than 600 carotenoids provide yellow, orange, and red colors in fruits and vegetables.
Carotenoids act as antioxidants in your body. This means they tackle harmful free radicals that damage tissues throughout your body.
The types of carotenoids that may have other health benefits include: Alpha-carotene, beta-carotene, and beta-cryptoxanthin. Your body can convert all of these to vitamin A. This vitamin helps keep your immune system working properly, and it’s needed for eye health. Yellow and orange foods like pumpkins and carrots are good sources of alpha- and beta-carotene.
These also contain beta-cryptoxanthin, as do sweet red peppers.
Lycopene. This gives red or pink color to: Tomatoes Watermelon and Pink grapefruit.
Lycopene has been linked to a lower risk of prostate cancer.
Lutein and zeaxanthin. These may help protect you from cataracts and age-related macular degeneration, which are two types of eye problems.
Good sources of these phytonutrients are greens such as: Spinach Kale and Collards.
Ellagic acid is found in a number of berries and other plant foods, especially: Strawberries, Raspberries and Pomegranates.
Ellagic acid may help protect against cancer through several different ways. For example, it may cause cancer cells to die. And it may help your liver neutralize cancer-causing chemicals in your system.
Flavonoids
A large number of phytonutrients fall into the flavonoid category. They are found in a variety of plant foods.
The types of flavonoids include: Catechins. Green tea is an especially good source of catechins. The drink may help prevent certain types of cancer.
Hesperidin. Found in citrus fruits, this flavonoid works as an antioxidant. It can reduce inflammation in the body. It may also help reduce the risk of cancer.
Flavonols. Quercetin is a well-studied type of flavonol. It is found in: Apples, Berries Grapes and Onions.
It might help reduce people’s risk of asthma, certain types of cancer, and coronary heart disease.
Resveratrol
Resveratrol is found in: Grapes, Purple grape juice and Red wine.
It acts as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory. Some research suggests that resveratrol might reduce the risk of heart disease and cancer. And it may help extend people’s life span.
Glucosinolates. Glucosinolates are found in cruciferous vegetables, including: Brussels sprouts Cabbage Kale and Broccoli.
They give these vegetables their sharp odor and flavor. The glucosinolates turn into other chemicals during the cooking process and while you digest these foods. These chemicals may help hold in check the development and growth of cancer.
Phytoestrogens
Phytoestrogens can behave in the body like the hormone estrogen. They can also block the effects of your natural supply of estrogen.
Soy foods contain isoflavones — a type of phytoestrogen. Some evidence suggests that soy foods may be linked to: Lower risk of endometrial cancer and Lower risk of bone loss in women.
Your body converts lignans, another type of phytonutrient, into chemicals with some estrogen-like effects. Two especially good sources of lignans are: Flaxseeds and Sesame seeds.
What Plant Colors mean with Phytonutrients
Recent Posts
Categories
Archives
- October 2024
- July 2022
- June 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- August 2019
- July 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- June 2016
- April 2015
- December 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- November 2013
- September 2013


